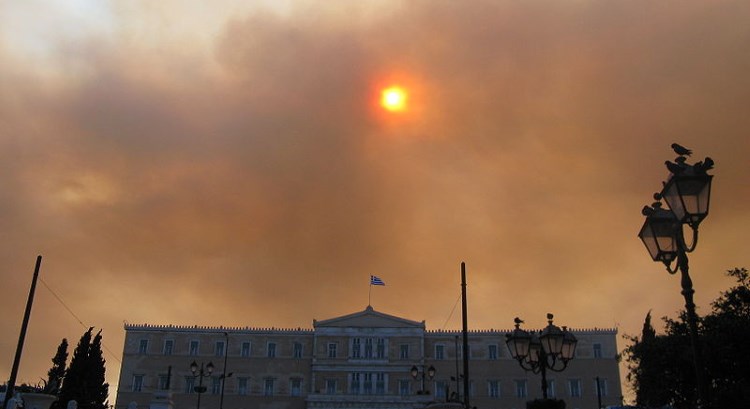
In a stark warning to EU officials, a new report by European Environment Agency (EEA) says, air pollution has significant impacts on the health of Europeans, especially in urban areas. According to EEA, air quality slowly improves but air pollution remains the single largest environmental health hazard in Europe.
Air quality reduces the quality of life in Europe, causes illnesses an results around 467.000 premature deaths each year. 430 000 of these deaths are within the EU.
85% Exposed to harmful emissions over WHO limits
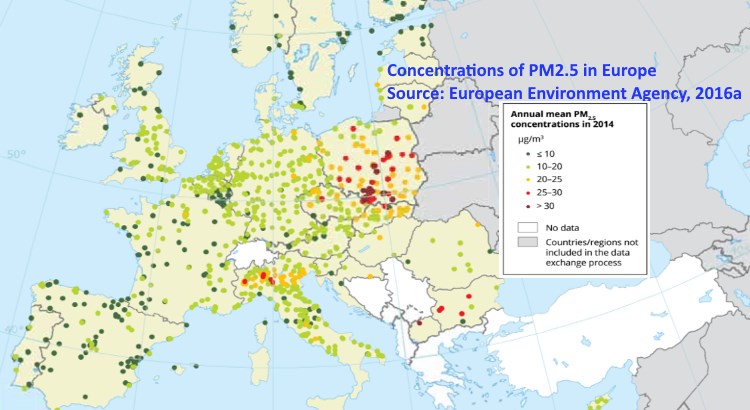
EEA’s report titled ‘Air Quality in Europe – 2016 report’ draws conclusions from official air quality monitoring stations in 41 European countries (thus also from non-EU) & over 400 cities from the year 2000 to 2014. The report shows that in 2014, 85% of urban population in Europe were exposed to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) at levels deemed harmful to health by the World Health Organization (WHO). Particulate matter can cause or aggravate cardiovascular diseases, asthma and lung cancer and the PM2.5s are the worst.
What are those “Particulate Matter”s or PMs?
“Particulate Matters” or “PM”s are microscopic solid or liquid matter suspended in the Earth’s atmosphere. They have impacts on climate and harmful to human health. Particulates are the deadliest form of air pollution due to their ability to penetrate deep into the lungs and blood streams unfiltered, causing permanent DNA mutations, heart attacks, and premature death.
PMs are further classified based on their sizes: PM10 (or PM10) is used to describe the air pollution composed of particles with a diameter of 10 micrometer (1/1000 of milimeter or one millionth of a meter). A 2013 study involving 312,944 people in nine European countries revealed that there was no safe level of particulates and that for every increase of 10 μg/m3 in PM10, the lung cancer rate rose 22%.
Then you have the PM2.5 (or PM2.5). It means the particles are very fine ones with a diameter of 2.5 μm or less. They are particularly deadly, with a 36% increase in lung cancer per 10 μg/m3 as it can penetrate deeper into the lungs.
Agriculture, coal, biomass….
The report also mentions that
- 16% of EU urban population are exposed to NO2 concentrations above the identical WHO and EU standards, with 94 % of these occurring due to traffic.
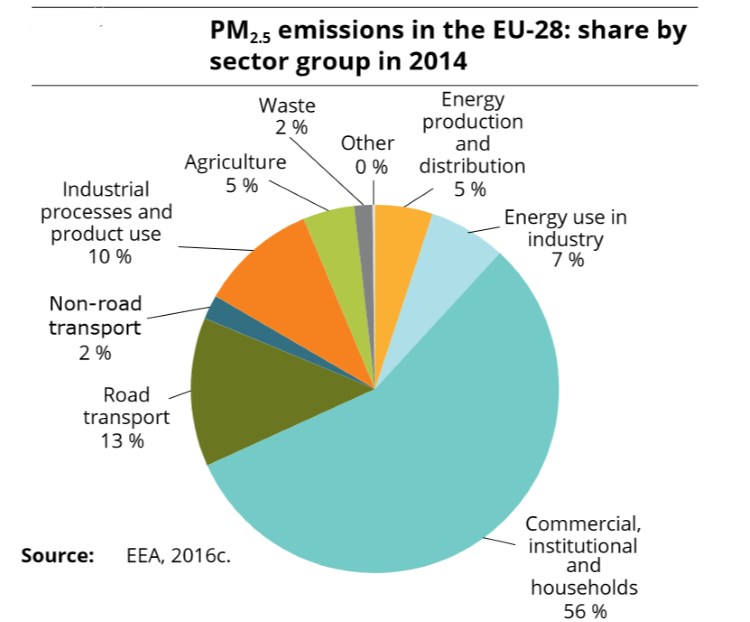
- PM2.5 emissions from coal and biomass combustion in households and from commercial and institutional buildings have not decreased to any significant degree. For a lower emissions in these areas, it is essential to fully implement measures in directives.
- Emissions of ammonia (NH3) from agriculture remain high and contribute especially to sustained PM levels and a number of high-PM episodes in Europe.
- Air pollution continues to damage vegetation and ecosystems. In this context, the most harmful air pollutants are O3, NH3 and NOx.
Go Deeper:
‘Air Quality in Europe – 2016 report’ European Environment Agency (EEA)
Image Credits:
Air pollution Smoke over Sintagma square in Athens Greece
by Юкатан / CC BY-SA ()
Map & Pie Chart from: European Environment Agency , Áir Quality in Europe – 2016 report’.